The Future of Smart Homes: The Technology Powering the Next Generation of Modern Living

 “`html
“`html
Introduction to Smart Homes
Smart homes, in essence, refer to residences equipped with advanced automation systems that enable the control of various household functions remotely or automatically. These systems can include devices, appliances, and features that communicate with one another through a network, often managed from a central hub or smartphone app. The scope of smart homes spans a broad range of functionalities, from basic lighting control and heating management to sophisticated security systems and health monitoring appliances.
The concept of smart homes dates back several decades, with initial advancements in home automation emerging in the latter half of the 20th century. Early adaptations were limited to standalone devices such as programmable thermostats and timed lighting systems, offering users a glimpse into the potential for enhanced residential convenience. However, the real evolution of smart homes began in the 21st century, driven by leaps in wireless technologies, the Internet of Things (IoT), and artificial intelligence. This progression has given rise to fully integrated and intelligent systems capable of learning user preferences, optimizing energy usage, and providing robust security measures.
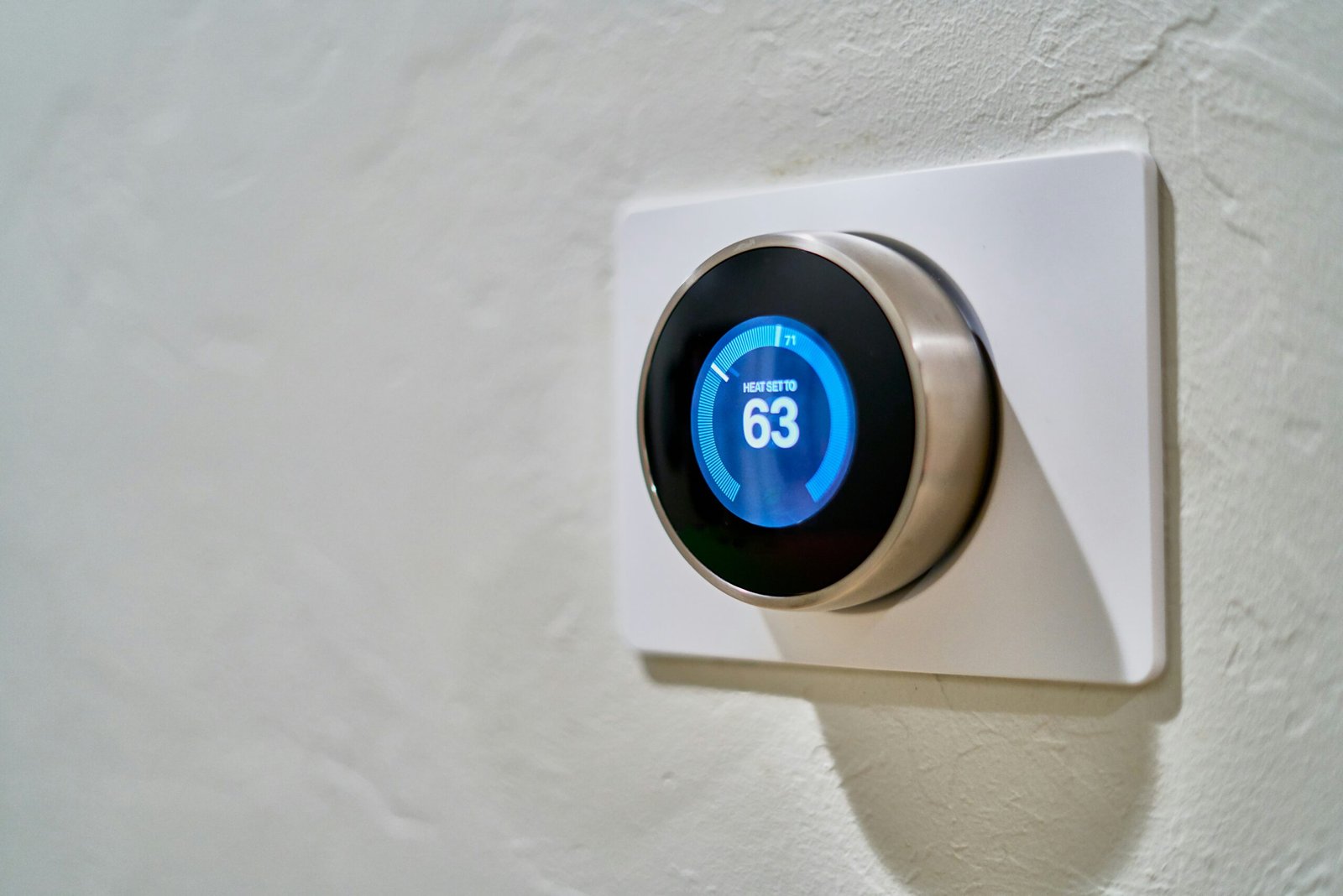
The benefits of smart homes are manifold. One of the primary advantages is the significant enhancement of convenience. With the ability to control various aspects of a home through a single interface, residents can easily manage their environment to suit their needs, whether they are home or away. Additionally, smart home systems contribute to energy efficiency by optimizing the use of household appliances and reducing wastage. For example, smart thermostats can learn a user’s schedule and adjust the temperature accordingly, ensuring comfort while minimizing energy consumption.
Improved security is another key benefit of smart homes. Advanced security systems can include features such as remote surveillance, automatic locking mechanisms, and real-time alerts, offering homeowners peace of mind and enhanced protection against potential threats. As technology continues to advance, the capabilities of smart homes are expected to expand even further, shaping the future of modern living in profound ways.
“`
The Role of the Internet of Things (IoT) in Smart Homes
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a transformative technology that serves as the backbone of modern smart homes. At its core, IoT refers to a network of interconnected devices that communicate and exchange data to function harmoniously within a single ecosystem. This communication occurs through the internet or other decentralized networks, enabling seamless integration and automated management of home systems. As IoT continues to evolve, its influence on the development and sophistication of smart homes becomes increasingly significant.
Within a smart home, IoT devices are designed to enhance convenience, security, and energy efficiency. Smart thermostats, for instance, use sensors and internet connectivity to regulate home temperatures based on the occupants’ preferences and routines, thereby optimizing energy consumption. Similarly, smart lighting systems can be programmed to adjust illumination based on time of day, occupancy, or even external environmental conditions, contributing to both energy savings and improved living comfort.
Security is another pillar of smart home technology, significantly bolstered by IoT devices. Examples include smart security cameras and doorbell cameras, which provide real-time video feeds and alerts to homeowners’ smartphones, no matter their location. These devices often feature advanced capabilities, such as facial recognition, motion detection, and integration with broader home security systems, ensuring comprehensive protection.
The interaction and communication between these IoT devices within a smart home is typically managed via central hubs or controllers, often using platforms like Amazon Alexa, Google Home, or Apple HomeKit. These central systems consolidate various devices and protocols under a unified user interface, allowing for seamless control and automation.
Furthermore, the data collected by IoT devices is pivotal to enhancing smart home functionalities. Temperature preferences, lighting usage patterns, and security breaches generate valuable data, which can be analyzed to further refine and personalize the home’s automation settings. However, the increasing amount of data also raises questions regarding privacy and security, necessitating robust data management and protection infrastructures.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning in Smart Homes
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are pivotal technologies driving the next frontier of smart homes. These advanced technologies enable smart home devices to adapt, learn, and ultimately enhance user experiences through personalized automation. AI and ML work together to analyze data from various smart devices, understanding user behaviors and preferences to make informed predictions and adjust home settings accordingly.
One primary application of AI in smart homes is through voice assistants, such as Amazon’s Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri. These AI-powered devices recognize natural language commands and interact seamlessly with other smart appliances, allowing homeowners to control lights, thermostats, and even coffee makers with simple voice prompts. Beyond convenience, these assistants learn from interactions, refining their responses and anticipating user needs over time.
Another area where AI and ML make significant impacts is within smart appliances. Smart refrigerators can keep inventory of food items, recommend grocery lists, and even suggest recipes based on available ingredients. AI-driven washing machines adjust their cycles based on the fabric type and load size, optimizing water and energy consumption. The incorporation of ML algorithms allows these devices to anticipate user habits, making them more efficient and user-friendly.
Security is also vastly improved through AI integration. Advanced security systems employ AI to identify unusual activities through pattern recognition, distinguishing between normal and suspicious behaviors. These systems can alert homeowners in real time, enhancing safety and providing peace of mind. Facial recognition technology, powered by AI, adds an additional layer of security by ensuring that only authorized individuals gain access.
AI and ML are not only transforming how we interact with our homes but also shaping a future where our living spaces adapt proactively to our daily routines. As these technologies continue to evolve, their applications in smart homes will become even more sophisticated, making modern living more comfortable, secure, and efficient.
“`html
Energy Management and Sustainability in Smart Homes
Smart home technology plays a crucial role in advancing energy management and sustainability. Among the pivotal innovations are smart thermostats, which have transformed how homeowners regulate their indoor climate. These devices learn user preferences and adjust heating and cooling settings automatically, ensuring optimal energy usage. For instance, by reducing heating when a home is unoccupied, smart thermostats minimize unnecessary energy consumption, resulting in lower utility bills and reduced carbon emissions.
Another significant advancement is smart lighting. Unlike traditional lighting systems, smart bulbs and lighting solutions can be controlled remotely via smartphone apps or voice commands. These lights can be programmed to turn on or off based on occupancy or time schedules, drastically reducing energy waste. Additionally, smart lighting systems often utilize LED technology, which is inherently more energy-efficient and longer-lasting compared to conventional bulbs.
Home energy management systems (HEMS) integrate with various smart devices to provide a comprehensive overview of energy consumption within a household. These systems allow homeowners to monitor energy use in real-time, identify energy-hogging appliances, and make informed decisions to enhance efficiency. By adopting HEMS, families can track their energy footprint and actively contribute to a sustainable living environment by making adjustments based on detailed consumption data.
The environmental impact of smart homes extends beyond energy savings. By optimizing energy usage and embracing renewable energy sources, smart homes decrease the reliance on fossil fuels. This shift not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also promotes a more sustainable energy infrastructure. For example, integrating solar panels with smart inverters into a household’s energy management system can optimize the use of solar energy, store excess power, and minimize energy drawn from the grid during peak hours.
Overall, the adoption of smart home technologies signifies a proactive step towards sustainability. By leveraging intelligent devices and systems that optimize energy consumption, homeowners are not just reducing their electricity bills but also contributing significantly to environmental conservation and the reduction of carbon footprints. As these technologies continue to evolve, they hold the promise of creating a greener and more sustainable future for all.
“`
Home Security and Privacy in the Age of Smart Homes
In recent years, advancements in smart home technology have significantly transformed the landscape of home security. The proliferation of devices such as smart locks, security cameras, and alarm systems offers homeowners unprecedented levels of control and peace of mind. Smart locks, for instance, provide not only convenience but also enhanced security by allowing homeowners to lock and unlock doors via their smartphone, control access with temporary digital keys, and receive notifications of any unauthorized entry attempts.
Security cameras are another crucial component of the smart home ecosystem. Modern smart cameras boast high-definition video quality, motion detection, night vision capabilities, and in some cases, facial recognition technology. These systems often integrate with home automation platforms, enabling users to monitor their home in real-time from any location. Alarm systems have also seen significant upgrades, now incorporating smart sensors that can detect unauthorized entry, fire, smoke, and even water leaks, sending instant alerts to the homeowner.
While the implementation of smart technology has enhanced security, it has also introduced new challenges related to privacy. Given that many smart devices collect and store vast amounts of personal data, potential security risks cannot be ignored. Homeowners must remain vigilant about protecting their data from unauthorized access and breaches. This includes adopting strong, unique passwords, regularly updating firmware, and utilizing reputable security solutions. Manufacturers often provide data encryption and robust security protocols, which should be enabled to fortify privacy further.
Another pertinent measure is to ensure the secure configuration of home networks. Employing a dedicated, encrypted network for smart devices can mitigate risks. Regular audits of devices and permissions can also help in identifying and correcting vulnerabilities. As smart homes continue to evolve, maintaining a balance between convenience, security, and privacy will be critical for homeowners investing in this technology.
The Integration of Smart Home Ecosystems
The integration of smart home ecosystems plays a crucial role in advancing modern living by enabling a seamless interaction between various devices and systems. There are multiple platforms and protocols designed to ensure compatibility and facilitate communication among smart home devices. Among the most notable standards are Zigbee, Z-Wave, and the newly introduced Matter protocol. Each of these frameworks brings its own set of advantages aimed at enhancing the user experience and simplifying the management of connected devices.
Zigbee is a widely adopted wireless communication protocol that allows various smart home devices, such as lights, thermostats, and sensors, to interoperate effectively. Operating on a mesh network, Zigbee ensures that the devices can communicate indirectly by passing data through a network of nodes, thereby increasing network reliability and range. This protocol is known for its low power consumption, making it a preferred choice for battery-operated devices.
Similarly, Z-Wave offers an alternative communication platform, also operating on a mesh network. With a different frequency band than Zigbee, Z-Wave minimizes potential interference from other wireless devices, ensuring stable and consistent performance. The proprietary nature of Z-Wave ensures rigorous certification processes, resulting in high compatibility among certified devices.
Matter, the latest entrant in the field, aims to unify the smart home ecosystem by offering a universal communication standard. Backed by industry giants such as Apple, Google, and Amazon, Matter focuses on resolving compatibility issues and simplifying the user onboarding process. This protocol is designed to function seamlessly across different networks, whether they are based on Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or Thread. As it gains adoption, Matter is expected to streamline smart home integrations even further.
Central hubs and smart home applications play indispensable roles in orchestrating a unified smart home experience. These central systems act as the nerve center of smart home ecosystems, enabling users to control multiple devices from a single interface. Popular examples include Amazon Echo, Google Nest Hub, and Apple HomePod, which support a variety of devices across different platforms. Through these central hubs, homeowners can execute complex automation scenarios, manage device settings, and monitor their smart home’s status in real-time with ease.
In conclusion, the integration of smart home ecosystems is essential for creating a cohesive and efficient smart home environment. Through the use of protocols like Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Matter, along with central hubs and smart home apps, users can experience a truly interconnected and streamlined modern living experience.
Challenges and Considerations for Smart Home Adoption
As the allure of smart homes continues to rise, various challenges and considerations complicate their widespread adoption. One primary hurdle is the cost of smart home devices. High-end systems and gadgets often come with a significant price tag, making them less accessible to average consumers. While the market is gradually offering more affordable options, the initial investment remains a barrier for many.
Technical issues also pose significant challenges. The reliability of smart home technologies can be undermined by software glitches, hardware malfunctions, and connectivity problems. These issues often require a certain level of technical know-how to troubleshoot, presenting a steep learning curve for users new to smart home ecosystems. This complexity can lead to frustration and may deter potential adopters from fully embracing smart home innovations.
Data privacy and security are paramount concerns in the realm of smart home technology. The interconnected nature of these systems often necessitates the collection and sharing of personal data, creating vulnerabilities that can be exploited by cybercriminals. Ensuring robust security measures and maintaining user trust are critical for the sustainable growth of smart home technology. Consumers must be vigilant about the security features of their devices and adhere to best practices for safeguarding their systems.
In addition to these concerns, standardization and interoperability among various smart home products remain significant issues. The lack of a unified protocol or standard can result in compatibility challenges, as devices from different manufacturers may not seamlessly integrate. This fragmentation can complicate the user experience, requiring multiple apps or hubs to control a variety of devices. A push towards more standardized solutions would enhance usability and foster greater adoption of smart home technologies.
Addressing these challenges is crucial for the future of smart homes. By tackling cost barriers, improving technical reliability, ensuring data security, and advancing standardization efforts, the industry can create a more accessible, secure, and cohesive smart home ecosystem.
The Future of Smart Homes: Predictions and Innovations
As we look toward the future of smart homes, several emerging technologies and innovations promise to revolutionize how we live. Foremost among these advancements is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI, with its capabilities for learning and adapting, is expected to drive the next generation of smart homes. By leveraging AI, homes will become more intuitive and personalized, understanding and predicting residents’ needs and preferences, thus enhancing not only convenience but also efficiency and energy management.
Another pivotal technology is edge computing, which processes data closer to the source of data generation rather than relying solely on centralized cloud servers. This approach significantly reduces latency, ensuring that smart home devices respond more swiftly and reliably. With edge computing, data privacy is also enhanced, as sensitive information can be kept nearer to the local network instead of being transmitted to potentially vulnerable cloud storage.
5G connectivity is another promising innovation set to impact the smart home landscape profoundly. The high-speed, low-latency communication enabled by 5G will facilitate seamless interactions among a plethora of connected devices. This will support the real-time data exchange necessary for sophisticated smart home ecosystems, making home automation more cohesive and comprehensive.
Looking ahead, several trends are emerging that could define the future of smart homes. Increasingly, there is a focus on health and wellness, with smart homes incorporating technologies that monitor and improve the wellbeing of occupants. From air purifiers and humidity regulators to sleep trackers and nutrition assistants, the emphasis on a healthier lifestyle is becoming more pronounced.
Smart homes are also playing a significant role in aging in place, allowing elderly individuals to maintain independence longer. Advanced monitoring systems, fall detection sensors, and user-friendly interfaces ensure safety and ease of use for senior residents. Moreover, these technologies provide family members and caregivers with peace of mind, knowing that assistance is readily available if needed.
Finally, the concept of fully autonomous homes is gaining traction. Imagine a home that operates autonomously, managing everything from climate control and security to cooking and cleaning through an interconnected web of smart devices. Such a level of automation could redefine modern living, offering unmatched convenience and efficiency.
In sum, the advancements in AI, edge computing, and 5G connectivity, combined with the emerging trends focused on health, aging in place, and home automation, paint an exciting picture of the future of smart homes. The journey toward fully autonomous living spaces reflects our evolving needs and technological progress, promising a future where our homes are not just smart, but truly intelligent.